Mountain instability monitoring
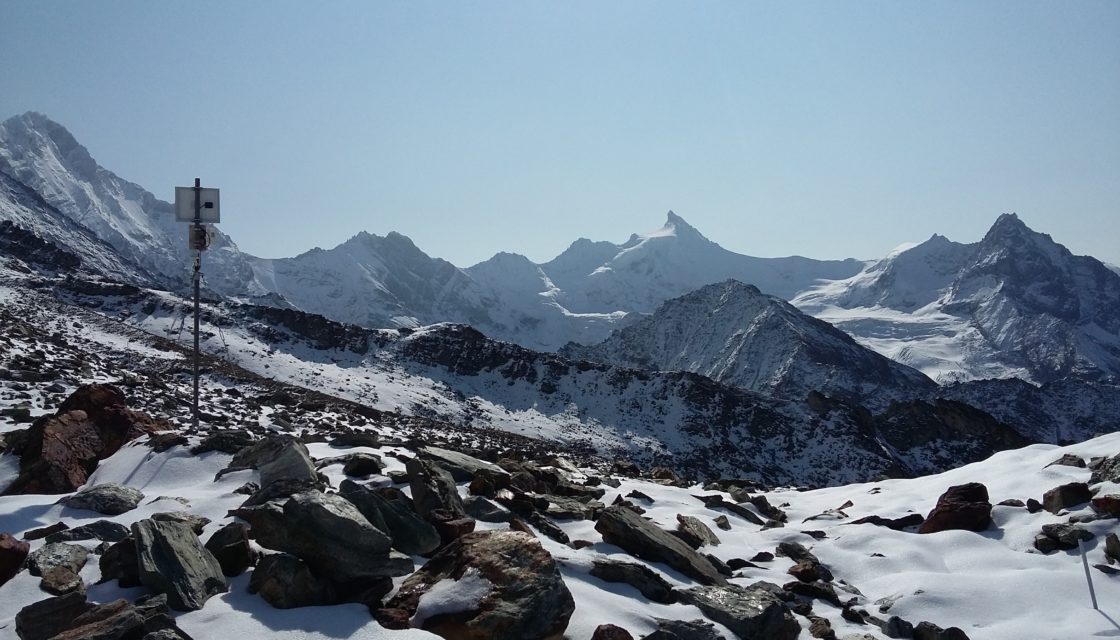

In alpine regions, the ability of icy soils to stabilize rocky slopes is diminishing, and water infiltration into the systems is increasing, changing the effective stresses. Today, there is an urgent need to better understand how certain natural hazards are triggered in the high mountains, and to develop new warning tools to improve risk management. The aim of the Monitoring des instabilités de haute montagne (MIHM) project , carried out by CREALP… Read More
GUARDAVAL monitoring system
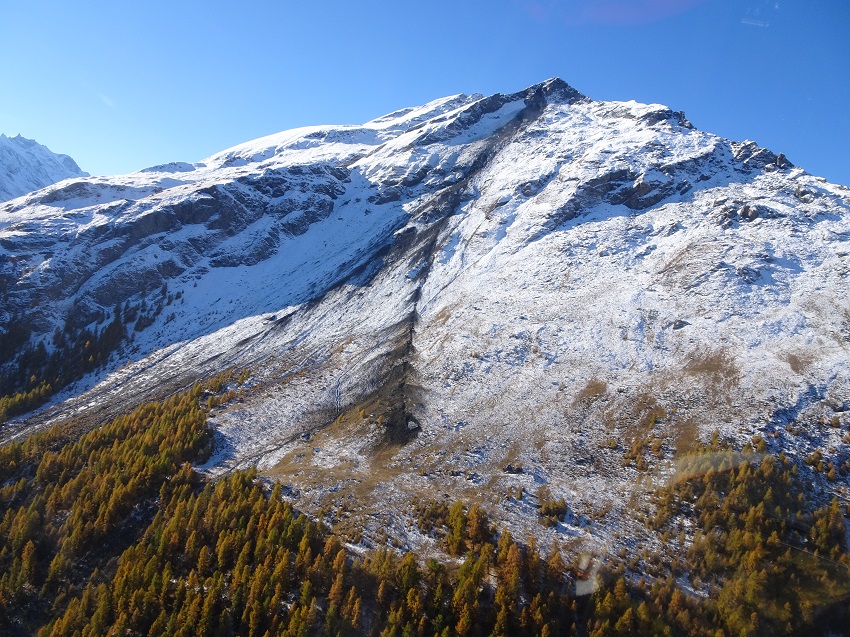

The Canton of Valais natural hazard monitoring portal Guardaval is a comprehensive IT platform for operational and synoptic monitoring of natural hazards (ground instabilities, floods, glacial hazards, meteorological hazards, debris flows, etc.) in the Valais. For over 20 years, CREALP has been maintaining and developing this constantly evolving platform for the State of Valais, integrating more data and functionalities every day. Today, Guardaval integrates more than 70 data sources from different suppliers… Read More
Geocadastre | geological surveys

Le cadastre cantonal des sondages géologiques – a web portal for consulting and editing subsoil data for the Canton of Valais Launched at the end of 2013, Géocadastre – the cantonal geological survey cadastre – has gradually established itself as a reference tool for practitioners. The Geocadast web portal not only enables consultation of subsurface data, but also provides information on the cantonal cadastre. The quaternary data contained in the Geocadastre are… Read More
Charriage + seismic sensors

SismoRiv project: Development of a charriage measurement system based on low-cost seismic sensors The aim of this project, which is dedicated to the issue of sediment transport, is to develop a measurement method that is simple to install and use, effective and considerably less costly for the various players involved (developers, risk managers, cantonal and municipal services). The monitoring of solid transport by watercourses is indeed of great economic and ecological importance…. Read More
Spatial Reference Information System | Floods
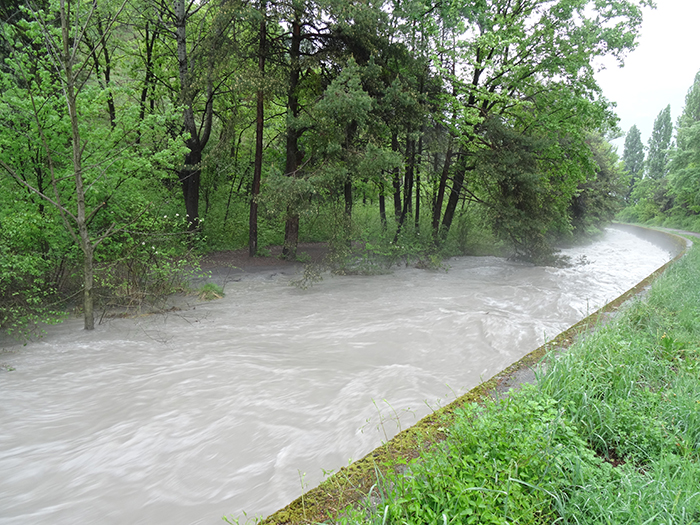

A Spatially Referenced Information System for managing hydrological hazards in the canton of Valais SIRS-CRUES is one of a series of spatially referenced information systems (SIRS) set up by the canton of Valais to optimize the use and enhancement of information contained in natural hazard studies (avalanches, floods, ground instabilities). SIRS-CRUES records information relating to hydrological hazards. Developed on the initiative of the Natural Hazards Service(SDANA) and with the collaboration of the… Read More
Exceptional and extreme floods (CRUEX ++)

A methodology for estimating exceptional and extreme floods in Switzerland The CRUEX++ “Exceptional and Extreme Floods” research project follows on from the CRUEX project, which in 2001 proposed a preliminary methodology of the PMP-PMF (Probable Maximum Precipitation-Probable Maximum Flood) type: a methodology for estimating extreme floods capable of integrating the hydrological particularities of the Alpine environment. As the quantitative estimation of extreme floods is still a poorly understood issue, this new project… Read More
RS MINERVE software
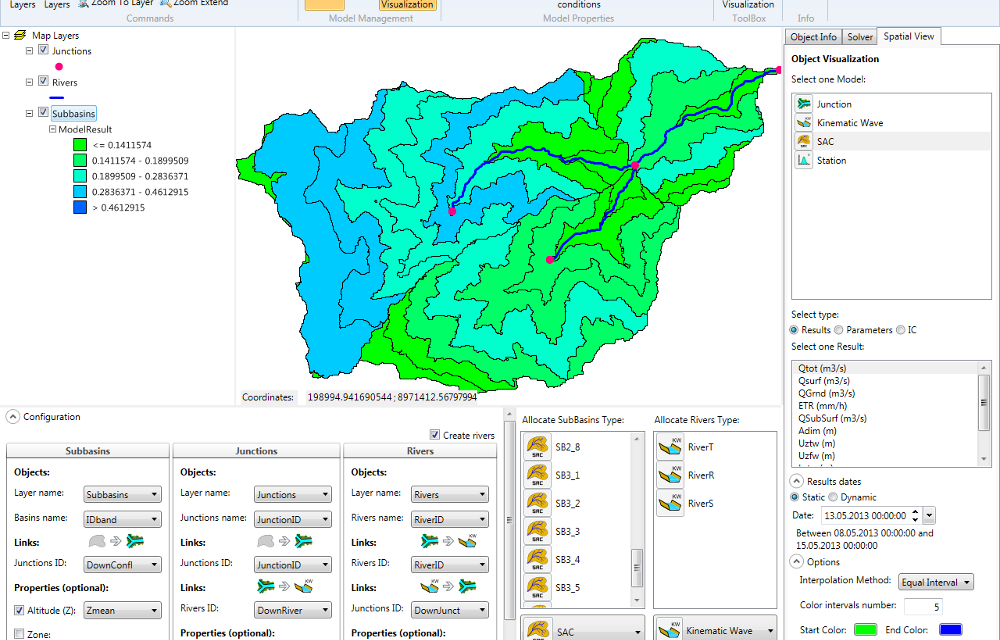
Modeling hydrological and hydraulic networks using a semi-distributed approach PRESENTATION RS MINERVE is a hydrological and hydraulic modeling software package that simulates rainfall-runoff transformations and free-surface flows. The software is capable of representing not only the main hydrological processes such as snowmelt, glacial melt and surface and subsurface flows, but also regulated structures such as reservoirs, gates, spillways, water intakes, turbines or pumps, and other hydraulic structures. Comprehensive analysis of a hydrological-hydraulic… Read More
Water resources management (Peru)
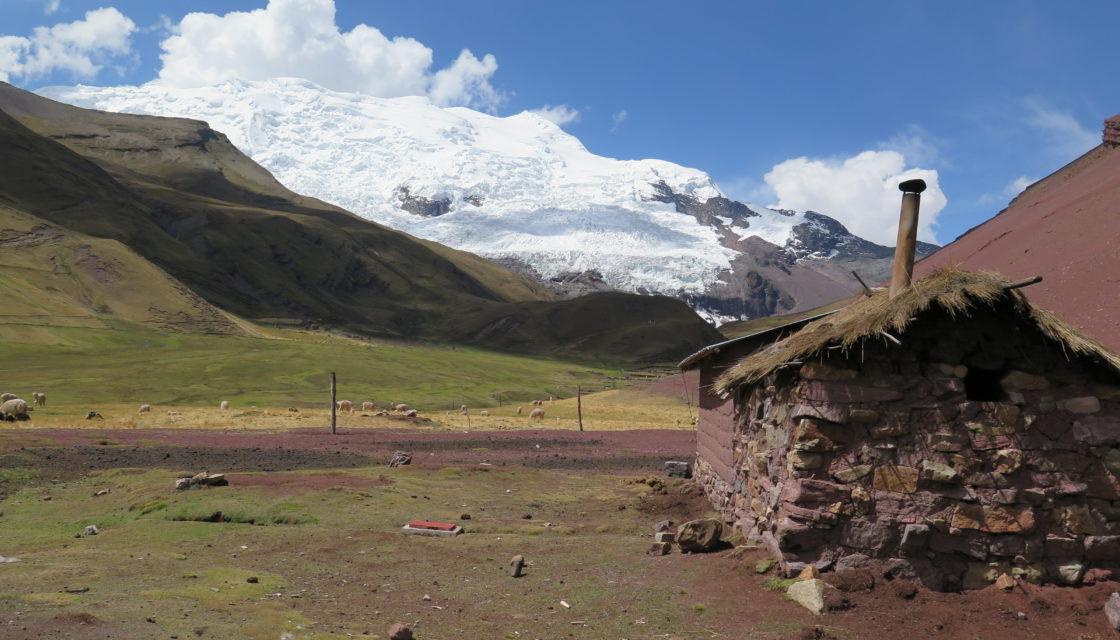

Glaciers + Project > Optimal management of water resources in mountain regions and in a context of climate change, Peru The multi-objective Glaciers+ project(Proyecto Glaciares+) was launched following the Glacier 513 project, which highlighted the potential of optimal water resource management in the Chucchún Valley. The aim of Glaciers+ was to reduce the risks associated with glacier retreat (flooding, block falls, etc.), and to optimize the management of water resources in mountain… Read More
Impact of climate change in the mountains: water resources and natural hazards (ATTENUATE)
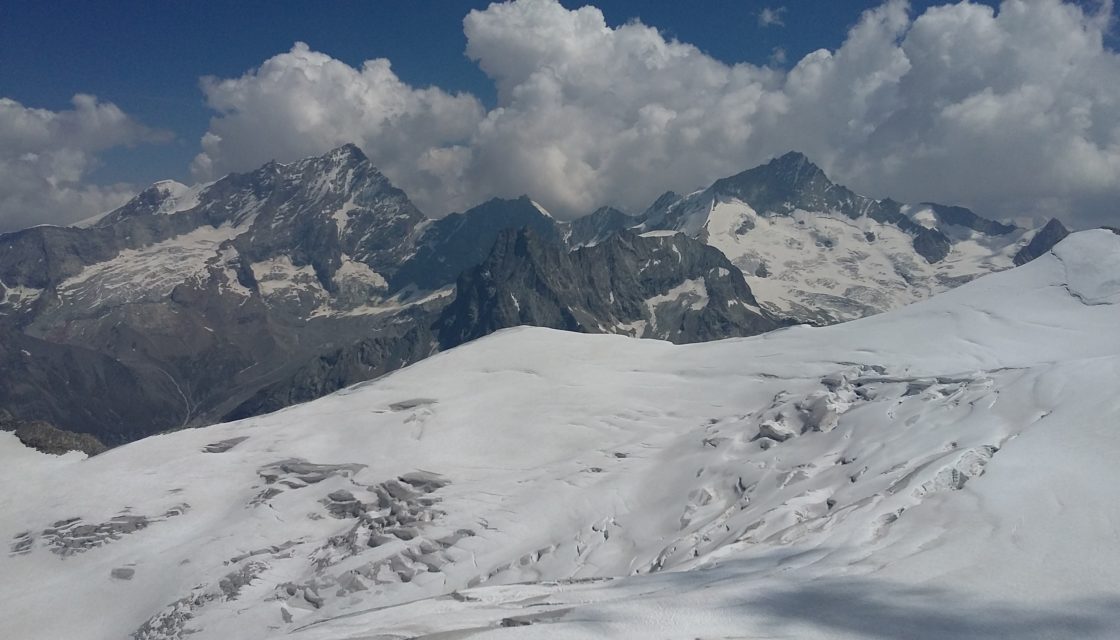

In the mountains, climate change is having a particularly severe impact on available water resources, leading to an increase in natural hazards. It is now necessary to improve knowledge and inform the public about the rapid changes taking place in Alpine environments. Warming in the Alps is twice as great as on a global scale, with direct consequences such as melting glaciers, degradation of permafrost and shorter periods of snow cover at… Read More
Support for groundwater protection zones

Support for the SEN in the approval procedure for groundwater protection zones to guarantee the quality of our drinking water In the Valais, drinking water is almost entirely supplied by groundwater reserves. It is therefore essential to ensure the quality of the water we consume. In order to guarantee the long-term protection of the groundwater that feeds the public interest catchments (springs and wells) used to supply the population with drinking water,… Read More
